Food & Climate
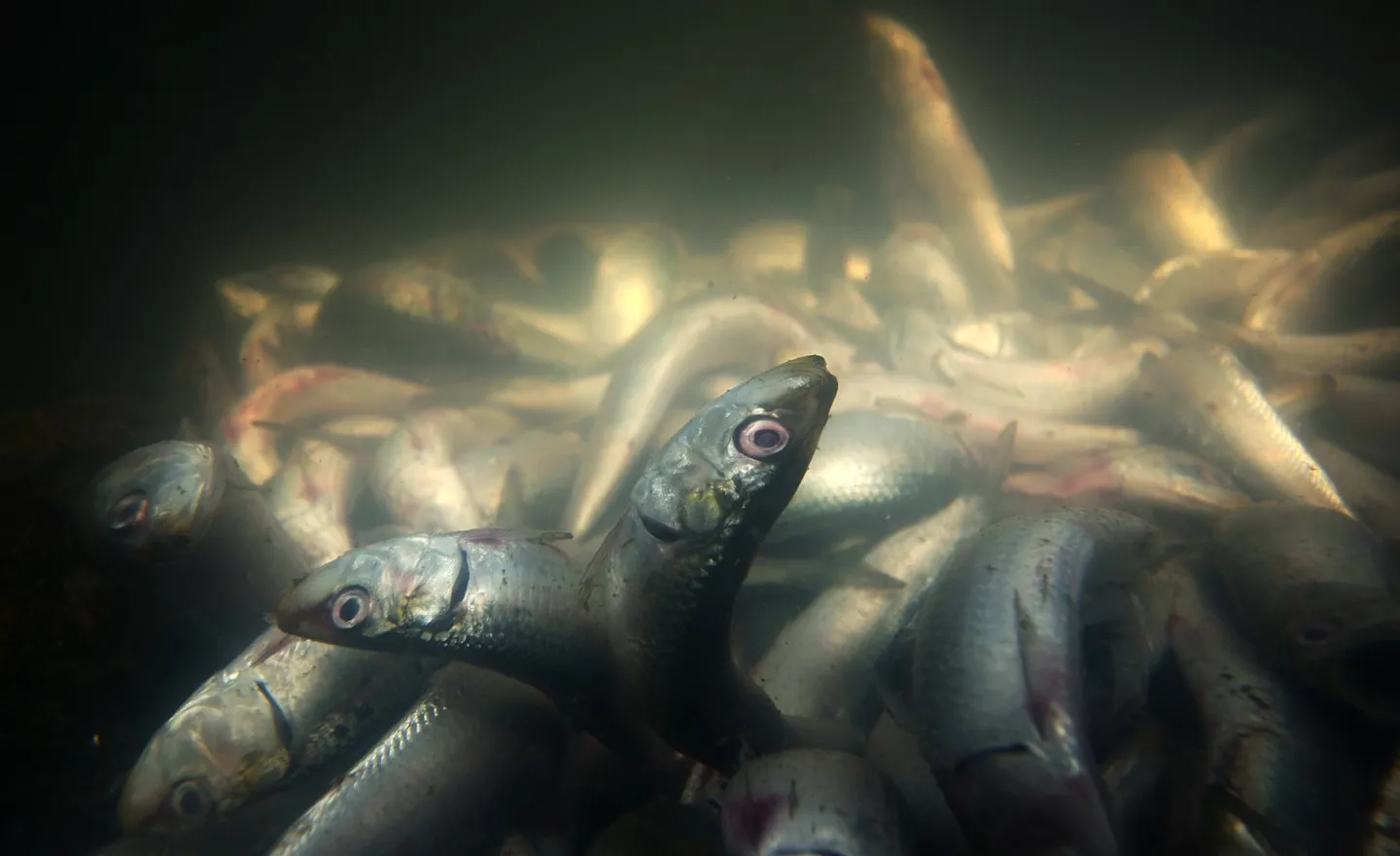
The government revealed the causes of the fish die-offs in Lake Manzala farms in Egypt, blaming climate change for the significant rise in temperature compared to the usual levels for this time of year.
A statement from the Ministry of Agriculture, obtained by “Food & Climate” platform on Sunday, August 10, 2025, indicated that Minister Alaa Farouk had instructed all agencies affiliated with the ministry to provide the necessary technical support to fish farmers.
The Ministry of Agriculture and Land Reclamation, represented by the Lakes Protection and Fish Resources Development Authority, issued a statement clarifying the scientific reasons behind the fish death in Lake Manzala farms, in response to circulating rumors that were recently monitored.
Some local media outlets and social media sites indicated that the lake had deteriorated since the 2000s, amid neglect that led to pollution, damage to biodiversity, and illegal acquisitions, to the point that it later became a hotbed of crime.
Despite the development of one of Egypt’s largest freshwater lakes, the old conditions that led to the lake’s deterioration are gradually returning, according to some Egyptian Facebook accounts.
Others have pointed to the dumping of sewage and industrial waste into Lake Manzala, which supplies fish farms run by state-owned fishermen.
The fish die-offs in Lake Manzala farms a natural phenomenon
The Lakes Protection and Fish Resources Development Authority stated that the fish die-offs in Lake Manzala farms in western Port Said Governorate are a natural phenomenon in light of climate change and the record-breaking temperatures currently being experienced worldwide.
A statement from the Ministry of Agriculture, represented by the Authority, added that fish are cold-blooded and directly affected by rising temperatures. Marine species farmed in Egypt, such as sea bream, sea bass, and grouper, are temperate-water fish, requiring temperatures between 20 and 24 degrees Celsius.
The statement continued, “This means that any increase or decrease in water temperature negatively impacts growth rates and the ability of these fish to cope with changes in water characteristics and their resistance to disease.”
The statement revealed that the Lake Manzala area has recently witnessed significant temperature increases, exposing fish farms to intense heat waves. This has caused water temperatures to rise beyond the appropriate temperature range for fish, causing fish stress and ultimately death.
The death of fish in Egypt’s Lake Manzala farms is also due to high temperatures, which lead to a lack of oxygen due to low dissolved oxygen levels in the water and high ammonia levels, affecting fish health, according to the government’s Lakes Protection and Fish Resources Development Agency.
The agency explained in a statement that changing water patterns and specifications increase fish stress in fish farms, as their storage density per unit volume of water is much higher than in the natural environments of these species.
The agency indicated that it is sparing no effort in providing all necessary technical support to educate fish farmers on how to cope with these climate phenomena and rising temperatures.
What is Lake Manzala in Egypt?
Manzala is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Egypt, with an area of 404.69 square kilometers and a depth of 1.15 meters.
It is located in the northeastern part of the Nile Delta and extends to connect with three governorates: Port Said, Dakahlia, and Damietta.
It shares its eastern border with the Suez Canal, is bordered to the west by the Damietta branch, and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, according to official data .
Lake Manzala is distinguished by its diverse landscape, containing both shallow and wide areas. The lake’s importance stems from its status as a habitat for migratory birds for breeding, watering, and food. It also contains various species of fish, such as tilapia, mullet, whitebait, grass carp, shrimp, and crab. The lake is also home to many different bird species. Lake Manzala is of great importance because it prevents seawater from entering and penetrating agricultural lands, acting as a barrier.
The data pointed to the numerous problems associated with the water supply to Lake Manzala, which prompted the decision to develop it in 2019.

It stated that there are several sources of water supplying the lake, including: the old and new El-Gamil Strait, the Diba Strait (El-Saffara), and the Ratma and El-Saffara Canals. The lake is also fed with mixed water through the saline section located in the Damietta branch, and through potable water.
This water comes from four sources: the Bahr El-Baqar Drain, which is a major source of sewage pollution in the lake; the El-Sarw Agricultural Drain, located in Damietta Governorate; the Hadous Agricultural Drain, which separates the governorates of Sharqia and Dakahlia; and the Ramses Drain, an agricultural drain located in Dakahlia Governorate.
The official data showed “The lake faces a number of problems and obstacles, including shrinking area due to erosion, dredging, and soil drying, as well as water pollution due to the discharge of wastewater, sewage, industrial and agricultural wastewater, and the growth of aquatic plants, such as water hyacinth and reeds, which has obstructed the flow of the lake’s water and affected its fish stocks.”

